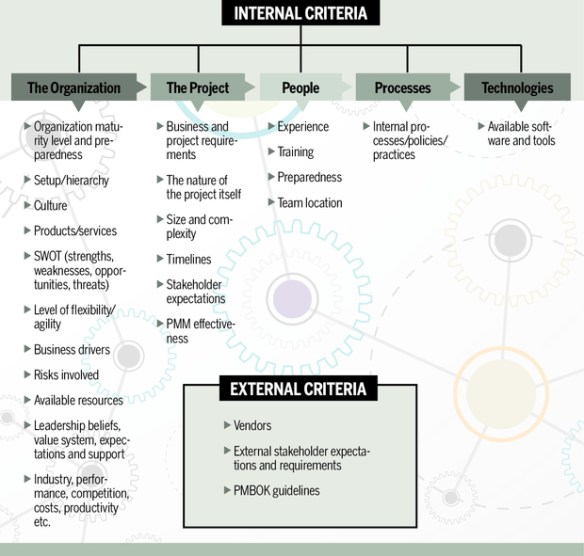
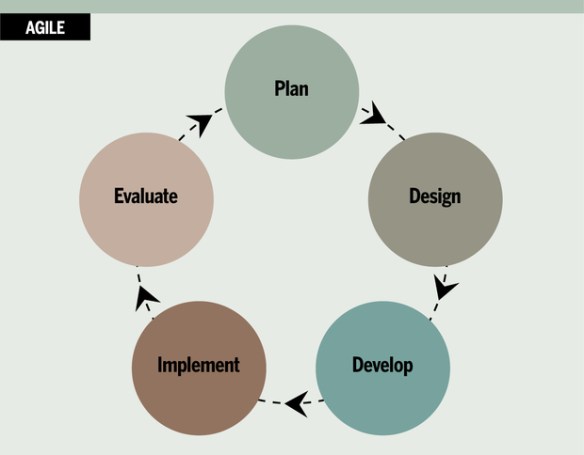
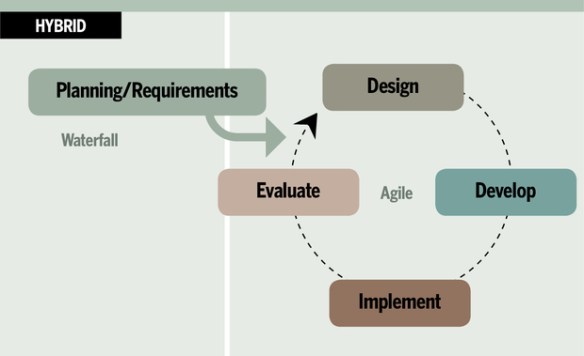
Project Time Management includes the processes required to manage the timely completion of the project.
download file excel : project-time-management
| Level 0 | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 |
| Project Time
Management |
|||
| Plan Schedule
Management |
|||
| Input | |||
| Project management plan | |||
| Project charter | |||
| Enterprise environmental factor | |||
| Organizational process asset | |||
| tools | |||
| Expert judgment | |||
| Analytical techniques | |||
| Meetings | |||
| Output | |||
| Schedule management Plan | |||
| Define activities | |||
| Input | |||
| Schedule management | |||
| Scope baseline | |||
| Enterprise environmental factor | |||
| Organizational process asset | |||
| tools | |||
| Decomposition | |||
| Rolling wave planning | |||
| Expert judgment | |||
| Output | |||
| Activity list | |||
| Activity attributes | |||
| Milestone list | |||
| Sequence Activities | |||
| Input | |||
| Schedule management | |||
| Activity list | |||
| Activity attributes | |||
| Milestone list | |||
| Project scope statement | |||
| Enterprise environmental factor | |||
| Organizational process asset | |||
| tools | |||
| Precedence diagramming | |||
| Dependency determination | |||
| Leads and lags | |||
| Output | |||
| Project schedule network | |||
| Project documents updates | |||
| Estimate activity resource | |||
| Input | |||
| Schedule management plan | |||
| Activity list | |||
| Activity attributes | |||
| Resource calendars | |||
| Risk register | |||
| Activity cost estimates | |||
| Enterprise environmental factors | |||
| Organizational process assets | |||
| tools | |||
| Expert judgment | |||
| Alternative analysis | |||
| Published estimating data | |||
| Bottom-up estimating | |||
| Project management software | |||
| Output | |||
| Activity resource requirements | |||
| Resource breakdown structure | |||
| Project documents updates | |||
| Estimate activity duration | |||
| Input | |||
| Schedule management plan | |||
| Activity list | |||
| Activity attributes | |||
| Activity resource requirements | |||
| Resource calendars | |||
| Project scope statement | |||
| Risk register | |||
| Resource breakdown structure | |||
| Enterprise environmental factors | |||
| Organizational process assets | |||
| tools | |||
| Expert judgment | |||
| Analogous estimating | |||
| Parametric estimating | |||
| Three-point estimating | |||
| Group decision-making echniques | |||
| Reserve analysis | |||
| Output | |||
| Activity duration estimates | |||
| Project documents updates | |||
| Develop Schedule | |||
| Input | |||
| Schedule management plan | |||
| Activity list | |||
| Activity attributes | |||
| Project schedule network diagram | |||
| Activity resource requirements | |||
| Resource calendars | |||
| Activity duration estimates | |||
| Project scope statement | |||
| Risk register | |||
| Project staff assignments | |||
| Resource breakdown structure | |||
| Enterprise environmental factors | |||
| Organizational process assets | |||
| tools | |||
| Schedule network analysis | |||
| Critical path method | |||
| Critical chain method | |||
| Resource optimization techniques (resource leveling, resource smoothing) | |||
| Modeling techniques (what if scenario analysis,simulation) | |||
| Leads and lags | |||
| Schedule compression (Crashing, Fast Tracking) | |||
| Scheduling tool | |||
| Output | |||
| Schedule baseline | |||
| Project schedule | |||
| Schedule data | |||
| Project calendars | |||
| Project management plan updates ( Schedule baseline,Schedule management plan,Cost baseline) | |||
| Project documents updates (Activity resource requirements,Activity attributes,Calendars,Risk register) | |||
| Control Schedule | |||
| Input | |||
| Project management plan | |||
| Project schedule | |||
| Work performance data | |||
| Project calendars | |||
| Schedule data | |||
| Organizational process assets | |||
| tools | |||
| Performance reviews (Trend analysis,Critical path method ,Critical chain method ,Earned value management) | |||
| Project management software | |||
| Resource optimization techniques | |||
| Modeling techniques | |||
| Leads and lags | |||
| Schedule compression | |||
| Scheduling tool | |||
| Output | |||
| Work performance information | |||
| Schedule forecasts | |||
| Change requests | |||
| Project management plan updates ( Schedule baseline,Schedule management plan,Cost baseline) | |||
| Project documents updates (schedule data, project schedule,risk register) | |||
| Organizational process assets updates | |||